 去看看
去看看

本指南为规范慢性乙型肝炎(CHB)的预防、诊断和抗病毒治疗而制定,涉及CHB其他治疗方法和策略请参阅相关的指南和共识。
中华医学会肝病学分会和感染病学分会于2005年组织国内有关专家制定了《慢性乙型肝炎防治指南》(第1版),并于2010年第1次修订。近5年来,国内外有关CHB的基础和临床研究取得很大进展,为此我们对本指南再次修订。
本指南旨在帮助临床医生在CHB诊断、预防和抗病毒治疗中做出合理决策,但不是强制性标准,也不可能涵盖或解决CHB诊治及管理中的所有问题。因此,临床医生在面对某一患者时,应在充分了解有关本病的最佳临床证据、认真考虑患者具体病情及其意愿的基础上,根据自己的专业知识、临床经验和可利用的医疗资源,制订全面合理的诊疗方案。我们将根据国内外的有关进展,继续对本指南进行不断更新和完善。
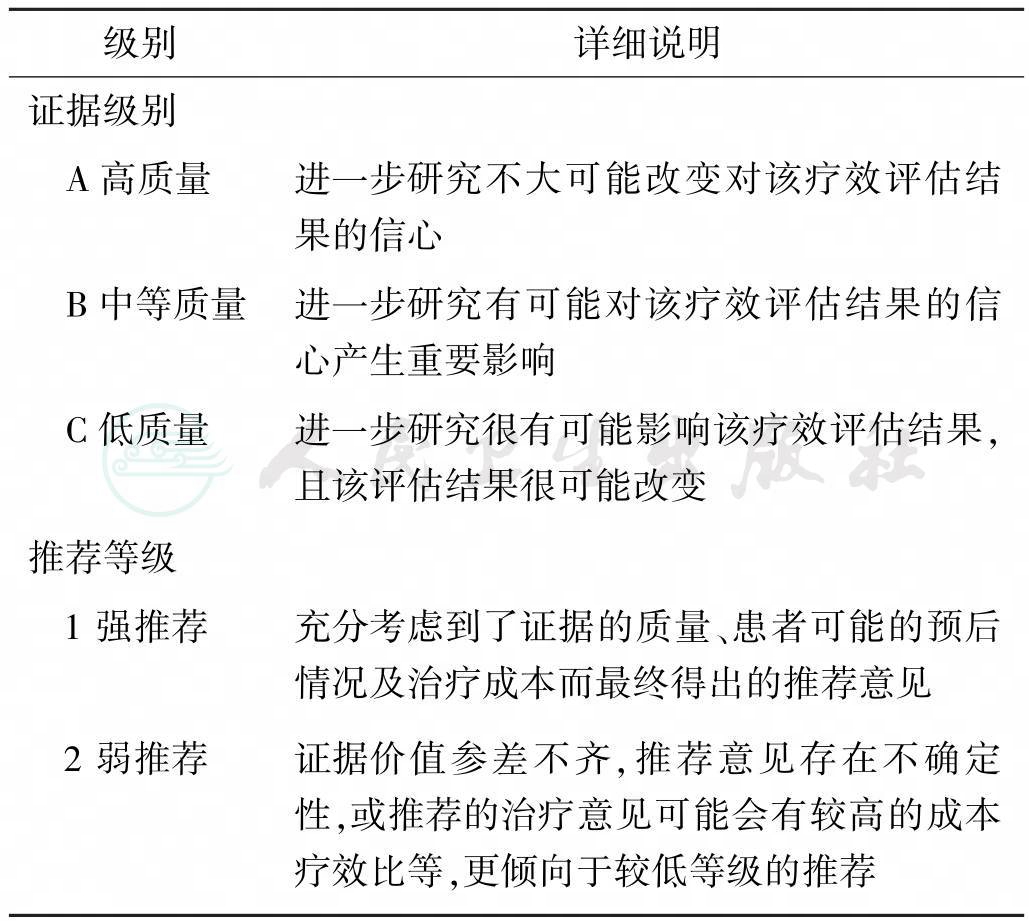
本指南中的证据等级分为A、B和C三个级别,推荐等级分为1和2两个级别(表1,根据GRADE分级修订)。
表1 推荐意见的证据等级和推荐等级
1 术语
慢性乙型肝炎病毒(HBV)感染(chronic HBV infection):HBsAg和(或)HBV DNA阳性6个月以上。
慢性乙型肝炎(chronic hepatitis B,CHB):由HBV持续感染引起的慢性肝脏炎症性疾病。可分为 HBeAg阳性 CHB和HBeAg阴性CHB。
HBeAg阳性慢性乙型肝炎(HBeAg positive CHB):血清HB-sAg阳性、HBeAg阳性、HBV DNA阳性,ALT持续或反复升高,或有肝组织学病变。
HBeAg阴性慢性乙型肝炎(HBeAg negative CHB):血清HBsAg阳性,HBeAg阴性,HBV DNA阳性,ALT持续或反复升高,或有肝组织学病变。
非活动性HBsAg携带者(inactive HBsAg carrier):血清HB-sAg阳性,HBeAg阴性,HBV DNA低于检测下限,1年内连续随访3次以上,每次至少间隔3个月,ALT均在正常范围。肝组织学检查显示:组织学活动指数(HAI)评分<4分或根据其他的半定量计分系统判定病变轻微。
乙型肝炎康复(resolved hepatitis B):既往有急性或CHB病史,HBsAg阴性,抗-HBs阳性或阴性,抗-HBc阳性,HBV DNA低于检测下限,ALT在正常范围。
慢性乙型肝炎急性发作(acute exacerbation or flare of hepatitis B):排除其他肝损伤因素后ALT升高至正常值上限(ULN)10倍以上。
乙型肝炎再活动(reactivation of hepatitis B):在HBV DNA持续稳定的患者,HBV DNA升高≥2log10 IU/ml,或基线HBV DNA阴性者由阴性转为阳性且≥100IU/ml,缺乏基线 HBV DNA者HBV DNA≥20 000IU/ml。往往再次出现ALT升高和肝脏炎症坏死。常发生于非活动性HBsAg携带者或乙型肝炎康复者,特别是在接受免疫抑制治疗或化疗时。
HBeAg阴转(HBeAg clearance):既往HBeAg阳性的患者HBeAg消失。
HBeAg血清学转换(HBeAg seroconversion):既往HBeAg阳性的患者HBeAg阴转,出现抗-HBe。
HBeAg逆转(HBeAg reversion):既往HBeAg阴性、抗-HBe阳性的患者再次出现HBeAg。
组织学应答(histological response):肝组织炎症坏死降低≥2分,且无肝纤维化评分的增高;或按Metavir评分,肝纤维化评分降低≥1分。
完全应答(complete response):持续??
[1]Ott JJ,Stevens GA,Groeger J,et al.Global epidemiology of hepatitis B virus infection:new estimates of age-specific HBsAg seroprevalence and endemicity[J].Vaccine,2012,30:2212-2219.
[2]Lozano R,Naghavi M,Foreman K,et al.Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010:a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010[J].Lancet,2012,380:2095-2128.
[3]Goldstein ST,Zhou F,Hadler SC,et al.A mathematical model to estimate global hepatitis B disease burden and vaccination impact[J].Int JEpidemiol,2005,34:1329-1339.
[4]Wang FS,Fan JG,Zhang Z,et al.The global burden of liver disease:Themajor impact of China[J].Hepatology,2014,60:2099-2108.
[5]Fung J,SetoW-K,Lai C-L,etal.Profiles of HBV DNA in a large population of Chinese patients with chronic hepatitis B:Implications for antiviral therapy[J].JHepatol,2011,54:195-200.
[6]Liang X,Bi S,Yang W,et al.Epidemiological serosurvey of hepatitis B in China--declining HBV prevalence due to hepatitis B vaccination[J].Vaccine,2009,27:6550-6557.
[7]Liang X,Bi S,Yang W,et al.Evaluation of the impact of hepatitis B vaccination among children born during 1992-2005 inChina[J].J Infect Dis,2009,200:39-47.
[8]Lu FM,Zhuang H.Management of hepatitis B in China[J]. Chin Med J(Engl),2009,122:3-4.
[9]WHO Guidelines Approved by the Guidelines Review Committee.Guidelines for the Prevention,Care and Treatment of Persons with Chronic Hepatitis B Infection[J].Geneva:World Health Organization,2015.
[10]Mast EE,Margolis HS,Fiore AE,et al.A comprehensive immunization strategy to eliminate transmission of hepatitis B virus infection in the United States:recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices(ACIP)part 1:immunization of infants,children,and adolescents[J].MMWR Recomm Rep,2005,54:1-31.
[11]中国疾病预防控制中心.乙肝疫苗儿童计划免疫技术管理规程(试行).2002.
[12]夏国良,龚健,王继杰,等.重组乙型肝炎疫苗阻断乙型肝炎病毒母婴传播方案的保护效果评价[J].中华流行病学杂志,2003,24:362-365.
[13]Singh AE,Plitt SS,Osiowy C,et al.Factors associated with vaccine failure and vertical transmission of hepatitis B among a cohort of Canadian mothers and infants[J].JViral Hepat,2011,18:468-473.
[14]Tran TT.Management of hepatitis B in pregnancy:weighing the options[J].Cleve Clin JMed,2009,76:S25-S29.
[15]Han L,Zhang HW,Xie JX,etal.Ameta-analysis of lamivudine for interruption of mother-to-child transmission of hepatitis B virus[J].World JGastroenterol,2011,17:4321-4333.
[16]Han GR,Cao MK,ZhaoW,et al.A prospective and open-label study for the efficacy and safety of telbivudine in pregnancy for the prevention of perinatal transmission of hepatitis B virus infection[J].JHepatol,2011,55:1215-1221.
[17]Pan CQ,Mi LJ,Bunchorntavakul C,et al.Tenofovirdisoproxil fumarate for prevention of vertical transmission of hepatitis B virus infection by highly viremic pregnant women:a case series[J].Dig Dis Sci,2012,57:2423-2429.
[18]Zanetti AR,Mariano A,RomanòL,et al.Long-term immunogenicity of hepatitis B vaccination and policy for booster:an I-talian multicentre study[J].Lancet,2005,366:1379-1384.
[19]Updated U.S.Public health service guidelines for themanagement of occupational exposures to HBV,HCV,and HIV and recommendations for postexposure prophylaxis[J].MMWR Recomm Rep,2001,50:1-52.
[20]Yan H,Zhong G,Xu G,etal.Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide is a functional receptor for human hepatitis B and D virus[J].Elife,2012,1:e00049.
[21]Liu CJ,Kao JH.Global perspective on the natural history of chronic hepatitis B:role of hepatitis B virus genotypes A to J [J].Semin Liver Dis,2013,33:97-102.
[22]Lin CL,Kao JH.The clinical implications of hepatitis B virus genotype:recent advances[J].JGastroenterol Hepatol,2011,26:123-130.
[23]Livingston SE,Simonetti JP,Bulkow LR,et al.Clearance of hepatitis B e antigen in patients with chronic hepatitis B and genotypes A,B,C,D,and F[J].Gastroenterology,2007,133:1452-1457.
[24]Yu MW,Yeh SH,Chen PJ,et al.Hepatitis B virus genotype and DNA level and hepatocellular carcinoma:a prospective study in men[J].JNatl Cancer Inst,2005,97:265-272.
[25]Lim SG,Cheng Y,Guindon S,et al.Viral quasi-species evolution during hepatitis Be antigen seroconversion[J].Gastroenterology,2007,133:951-958.
[26]Wang HY,Chien MH,Huang HP,etal.Distincthepatitis B virus dynamics in the immunotolerant and early immunoclearance phases[J].JVirol,2010,84:3454-3463.
[27]Liu F,Chen L,Yu DM,et al.Evolutionary patterns of hepatitis B virus quasispecies under different selective pressures:correlation with antiviral efficacy[J].Gut,2011,60:1269-1277.
[28]Lai CL,Ratziu V,Yuen MF,et al.Viral hepatitis B[J].Lancet,2003,362:2089-2094.
[29]Liaw YF.Natural history of chronic hepatitis B virus infection and long-term outcome under treatment[J].Liver Int,2009,29:100-107.
[30]Hui CK,Leung N,Yuen ST,et al.Natural history and disease progression in Chinese chronic hepatitis B patients in immunetolerant phase[J].Hepatology,2007,46:395-401.
[31]McMahon BJ.The natural history of chronic hepatitis B virus infection[J].Hepatology,2009,49:S45-S55.
[32]Liaw YF.Hepatitis flares and hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion:implication in anti-hepatitis B virus therapy[J].JGastroenterol Hepatol,2003,18:246-252.
[33]Chu CM,Hung SJ,Lin J,etal.Natural history of hepatitis B e antigen to antibody seroconversion in patientswith normal serum aminotransferase levels[J].Am J Med,2004,116:829-834.
[34]Chu CM,Liaw YF.Prevalence of and risk factors for hepatitis B viremia after spontaneous hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance in hepatitis B carriers[J].Clin Infect Dis,2012,54:88-90.
[35]Chu CM,Liaw YF.Hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance during chronic HBV infection[J].Antivir Ther,2010,15:133-143.
[36]Fattovich G,Bortolotti F,Donato F.Natural history of chronic hepatitis B:special emphasis on disease progression and prognostic factors[J].JHepatol,2008,48:335-352.
[37]Chen YC,Chu CM,Liaw YF.Age-specific prognosis following spontaneous hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion in chronic hepatitis B[J].Hepatology,2010,51:435-444.
[38]Park BK,Park YN,Ahn SH,et al.Long-term outcome of chronic hepatitis B based on histological grade and stage[J].J Gastroenterol Hepatol,2007,22:383-388.
[39]Lin SM,Yu ML,Lee CM,et al.Interferon therapy in HBeAg positive chronic hepatitis reduces progression to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma[J].JHepatol,2007,46:45-52.
[40]Yim HJ,Lok AS.Natural history of chronic hepatitis B virus infection:what we knew in 1981 and what we know in 2005 [J].Hepatology,2006,43:S173-S181.
[41]Chu CM,Liaw YF.Hepatitis B virus-related cirrhosis:natural history and treatment[J].Semin Liver Dis,2006,26:142-152.
[42]Chen YC,Chu CM,Yeh CT,et al.Natural course following the onset of cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B:a longterm follow-up study[J].Hepatol Int,2007,1:267-273.
[43]Hsu YS,Chien RN,Yeh CT,et al.Long-term outcome after spontaneous HBeAg seroconversion in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J].Hepatology,2002,35:1522-1527.
[44]McMahon BJ,Holck P,Bulkow L,et al.Serologic and clinical outcomes of 1536 Alaska Natives chronically infected with hepatitis B virus[J].Ann Intern Med,2001,135:759-768.
[45]Fattovich G,Giustina G,Schalm SW,et al.Occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma and decompensation in western European patients with cirrhosis type B.The EUROHEPStudy Group on Hepatitis B Virus and Cirrhosis[J].Hepatology,1995,21:77-82.
[46]Fattovich G.Natural history and prognosis of hepatitis B[J]. Semin Liver Dis,2003,23:47-58.
[47]Tseng TC,Liu CJ,Yang HC,et al.Serum hepatitis B surface antigen levels help predict disease progression in patientswith low hepatitis B virus loads[J].Hepatology,2013,57:441-450.
[48]Tseng TC,Liu CJ,Yang HC,et al.High levels of hepatitis B surface antigen increase risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with low HBV load[J].Gastroenterology,2012,142:1140-1149.
[49]DandriM,Locarnini S.New insight in the pathobiology of hepatitis B virus infection[J].Gut,2012,61:i6-17.
[50]Zhang Z,Zhang JY,Wang LF,et al.Immunopathogenesis and prognostic immunemarkers of chronic hepatitis B virus infection[J].JGastroenterol Hepatol,2012,27:223-230.
[51]Isogawa M,Tanaka Y.Immunobiology of hepatitis B virus infection[J].Hepatol Res,2015,45:179-189.
[52]Guidotti LG,Chisari FV.Noncytolytic control of viral infections by the innate and adaptive immune response[J].Annu Rev Immunol,2001,19:65-91.
[53]Bertoletti A,Ferrari C.Innate and adaptive immune responses in chronic hepatitis B virus infections:towards restoration of immune control of viral infection[J].Gut,2012,61:1754-1764.
[54]Fan R,Sun J,Yuan Q,et al.Baseline quantitative hepatitis B core antibody titre alone strongly predicts HBeAg seroconversion across chronic hepatitis B patients treated with peginterferon or nucleos(t)ide analogues[J].Gut,2016,65:313-320.
[55]Hou FQ,Song LW,Yuan Q,etal.Quantitative hepatitis B core antibody level is a new predictor for treatment response in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B patients receiving peginterferon[J].Theranostics,2015,5:218-226.
[56]Lampertico P,Maini M,Papatheodoridis G.Optimal Management of Hepatitis B Virus Infection-EASL Special Conference [J].JHepatol,2015,63:1238-1253.
[57]Liaw YF,Kao JH,Piratvisuth T,et al.Asian-Pacific consensus statement on the management of chronic hepatitis B:a 2012 update[J].Hepatol Int,2012,6:531-561.
[58]中华人民共和国卫生部.原发性肝癌诊疗规范(2011年版)摘要[J].中华肝脏病杂志,2012,20:419-426.
[59]Wong GL,Chan HL,Tse YK,et al.On-treatment alpha-fetoprotein is a specific tumormarker for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic hepatitis B receiving entecavir[J]. Hepatology,2014,59:986-995.
[60]Hann HW,Fu X,Myers RE,et al.Predictive value of alphafetoprotein in the long-term risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with hepatitis B virus infection--results from a clinic-based longitudinal cohort[J].Eur J Cancer,2012,48:2319-2327.
[61]Amaddeo G,Cao Q,Ladeiro Y,etal.Integration of tumour and viral genomic characterizations in HBV-related hepatocellular carcinomas[J].Gut,2015,64:820-829.
[62]Marrero JA,Su GL,Wei W,et al.Des-gamma carboxyprothrombin can differentiate hepatocellular carcinoma from nonmalignant chronic liver disease in american patients[J].Hepatology,2003,37:1114-1121.
[63]Inagaki Y,Tang W,MakuuchiM,et al.Clinical and molecular insights into the hepatocellular carcinoma tumourmarker desgamma-carboxyprothrombin[J].Liver Int,2011,31:22-35.
[64]Seo SI,Kim HS,Kim WJ,et al.Diagnostic value of PIVKA-Ⅱand alpha-fetoprotein in hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma[J].World J Gastroenterol,2015,21:3928-3935.
[65]WaiCT,Greenson JK,Fontana RJ,et al.A simple noninvasive index can predict both significant fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C[J].Hepatology,2003,38:518-526.
[66]Scott DR,Levy MT.Liver transient elastography(Fibroscan):a place in themanagementalgorithms of chronic viral hepatitis [J].Antivir Ther,2010,15:1-11.
[67]Shaheen AA,Wan AF,Myers RP.FibroTest and FibroScan for the prediction of hepatitis C-related fibrosis:a systematic review of diagnostic test accuracy[J].Am J Gastroenterol,2007,102:2589-2600.
[68]EASL-ALEH Clinical Practice Guidelines:Non-invasive tests for evaluation of liver disease severity and prognosis[J].J Hepatol,2015,63:237-264.
[69]肝脏硬度评估小组.瞬时弹性成像技术诊断肝纤维化专家意见[J].中华肝脏病杂志,2013,21:420-424.
[70]Jia J,Hou J,Ding H,et al.Transientelastography compared to serum markers to predict liver fibrosis in a cohort of Chinese patientswith chronic hepatitis B[J].JGastroenterol Hepatol,2015,30:756-762.
[71]Chang TT,Liaw YF,Wu SS,etal.Long-term entecavir therapy results in the reversal of fibrosis/cirrhosis and continued histological improvement in patientswith chronic hepatitis B[J]. Hepatology,2010,52:886-893.
[72]Marcellin P,Gane E,ButiM,etal.Regression of cirrhosis during treatment with tenofovirdisoproxil fumarate for chronic hepatitis B:a 5-year open-label follow-up study[J].Lancet,2013,381:468-475.
[73]LiW,Zhao J,Zou Z,et al.Analysis of hepatitis B virus intrahepatic covalently closed circular DNA and serum viralmarkers in treatment-naive patients with acute and chronic HBV infection[J].PLoSOne,2014,9:e89046.
[74]Bedossa P,Poynard T.An algorithm for the grading of activity in chronic hepatitis C.The METAVIR Cooperative Study Group[J].Hepatology,1996,24:289-293.
[75]Xu S,Wang Y,Tai DC,et al.qFibrosis:a fully-quantitative innovativemethod incorporating histological features to facilitate accurate fibrosis scoring in animal model and chronic hepatitis B patients[J].JHepatol,2014,61:260-269.
[76]Ding H,Ma JJ,Wang WP,et al.Assessment of liver fibrosis:the relationship between point shear wave elastography and quantitative histological analysis[J].JGastroenterol Hepatol,2015,30:553-558.
[77]Ganem D,Prince AM.Hepatitis B virus infection--natural history and clinical consequences[J].N Engl JMed,2004,350:1118-1129.
[78]European Association For The Study Of The Liver.EASL clinical practice guidelines:management of chronic hepatitis B virus infection[J].JHepatol,2012,57:167-185.
[79]科技部十二五重大专项联合课题组.乙型肝炎病毒相关肝硬化的临床诊断、评估和抗病毒治疗的综合管理[J].中华肝脏病杂志,2014,22:327-335.
[80]中华医学会肝病学分会,中华医学会感染病学分会,Association CM.慢性乙型肝炎防治指南(2010年版)[J].中华肝脏病杂志,2011,19:13-24.
[81]Arvaniti V,D’Amico G,Fede G,et al.Infections in patients with cirrhosis increase mortality four-fold and should be used in determining prognosis[J].Gastroenterology,2010,139:1246-1256,1256.e1-5.
[82]Tsochatzis EA,Bosch J,Burroughs AK.Liver cirrhosis[J]. Lancet,2014,383:1749-1761.
[83]Caviglia GP,Abate ML,Pellicano R,et al.Chronic hepatitis B therapy:available drugs and treatment guidelines[J].Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol,2015,61:61-70.
[84]Vallet-Pichard A,Pol S.Hepatitis B virus treatment beyond the guidelines:special populations and consideration of treatment withdrawal[J].Therap Adv Gastroenterol,2014,7:148-155.
[85]Tang CM,Yau TO,Yu J.Management of chronic hepatitis B infection:current treatment guidelines,challenges,and new developments[J].World J Gastroenterol,2014,20:6262-6278.
[86]Zhao H,Kurbanov F,Wan MB,et al.Genotype B and younger patient age associated with better response to low-dose therapy:a trial with pegylated/nonpegylated interferon-alpha-2b for hepatitis B e antigen-positive patientswith chronic hepatitis B in China[J].Clin Infect Dis,2007,44:541-548.
[87]Liaw YF,Jia JD,Chan HL,et al.Shorter durations and lower doses of peginterferon alfa-2a are associated with inferior hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion rates in hepatitis B virus genotypes B or C[J].Hepatology,2011,54:1591-1599.
[88]Buster EH,Flink HJ,Cakaloglu Y,etal.Sustained HBeAg and HBsAg loss after long-term follow-up of HBeAg-positive patients treated with peginterferon alpha-2b[J].Gastroenterology,2008,135:459-467.
[89]Marcellin P,Bonino F,Yurdaydin C,et al.Hepatitis B surface antigen levels:association with 5-year response to peginterferon alfa-2a in hepatitis B e-antigen-negative patients[J].Hepatol Int,2013,7:88-97.
[90]Lampertico P,Vigano M,Colombo M.Treatment of HBeAgnegative chronic hepatitis B with pegylated interferon[J].Liver Int,2011,31:90-94.
[91]Lampertico P,ViganòM,Di CGG,et al.Randomised study comparing 48 and 96 weeks peginterferonα-2a therapy in genotype D HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B[J].Gut,2013,62:290-298.
[92]Kim V,Abreu RM,Nakagawa DM,et al.Pegylated interferon alfa for chronic hepatitis B:systematic review and meta-analysis[J].JViral Hepat,2016,23:154-169.
[93]Wong GL,Wong VW,Chan HL.Combination therapy of interferon and nucleotide/nucleoside analogues for chronic hepatitis B[J].JViral Hepat2014,21:825-834.
[94]Marcellin P,Ahn S,Ma X,etal.HBsAg Losswith TenofovirD-isoproxil Fumarate(TDF)plus Peginterferon alfa-2a(PEG)in Chronic Hepatitis B(CHB):Results of a Global Randomized Controlled Trial[J].Hepatology,2014,60:294a-295a.
[95]Xie Q,Zhou H,Bai X,et al.A randomized,open-label clinical study of combined pegylated interferon Alfa-2a(40KD)and entecavir treatment for hepatitis B"e"antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B[J].Clin Infect Dis,2014,59:1714-1723.
[96]Chi H,Xie Q,Zhang N,et al.Addition of Peginterferon Alfa-2b During Long-term Nucleos(t)ide Analogue Therapy Increases HBeAg Seroconversion and HBsAg Decline-Week 48 Results From a Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial(PEGON Study)[J].Hepatology,2014,60:1106a-a.
[97]Ning Q,Han M,Sun Y,et al.Switching from entecavir to PegIFN alfa-2a in patientswith HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B:a randomised open-label trial(OSST trial)[J].JHepatol,2014,61:777-784.
[98]Hu P,Jia S,Zhang W,et al.A multi-center randomized study on the efficacy and safety of switching to peginterferon alpha-2a(40KD)for 48 or 96 weeks in HBeAg positive CHB patients with a prior NUC history for 1 to 3 years:an interim analysis of NEW SWITCH study[J].Hepatology,2014,60:1273a-1274a.
[99]BrouwerWP,Xie Q,Sonneveld MJ,etal.Adding pegylated interferon to entecavir for hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B:A multicenter randomized trial(ARES study)[J].Hepatology,2015,61:1512-1522.
[100]Li GJ,Yu YQ,Chen SL,et al.Sequential combination therapy with pegylatedinterferon leads to loss of hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B e antigen(HBeAg)seroconversion in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B patients receiving long-term entecavirtreatment[J].Antimicrob Agents Chemother,2015,59:4121-4128.
[101]Sonneveld MJ,Hansen BE,Piratvisuth T,et al.Responseguided peginterferon therapy in hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B using serum hepatitis B surface antigen levels[J].Hepatology,2013,58:872-880.
[102]SarriG,Westby M,Bermingham S,et al.Diagnosis and management of chronic hepatitis B in children,young people,and adults:summary of NICE guidance[J].BMJ,2013, 346:f3893.
[103]Rijckborst V,Hansen BE,Ferenci P,et al.Validation of a stopping rule at week 12 using HBsAg and HBV DNA for HBeAg-negative patients treated with peginterferon alfa-2a [J].JHepatol,2012,56:1006-1011.
[104]Chang TT,Gish RG,de Man R,et al.A comparison of entecavir and lamivudine for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B [J].N Engl JMed,2006,354:1001-1010.
[105]Lai CL,Shouval D,Lok AS,et al.Entecavir versus lamivudine for patientswith HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B[J]. N Engl JMed,2006,354:1011-1020.
[106]Chang TT,Lai CL,Kew YS,et al.Entecavir treatment for up to 5 years in patientswith hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B[J].Hepatology 2010,51:422-430.
[107]Tenney DJ,Rose RE,Baldick CJ,et al.Long-term monitoring shows hepatitis B virus resistance to entecavir in nucleosidenaive patients is rare through 5 years of therapy[J].Hepatology,2009,49:1503-1514.
[108]LokAS.Hepatitis:Long-term therapy of chronic hepatitis B reverses cirrhosis[J].Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol,2013,10:199-200.
[109]Marcellin P,Heathcote EJ,Buti M,et al.Tenofovirdisoproxil fumarate versus adefovir dipivoxil for chronic hepatitis B [J].N Engl JMed,2008,359:2442-2455.
[110]Marcellin PGE,Flisiak R,TrinhH,et al.Long term treatment with tenofovirdisoproxil fumarate for chronic hepatitis B infection is safe and well tolerated and associated with durable virologic response with no detectable resistance:8 year results from two phase 3 trials[J].Hepatology,2014,60:313A-314A.
[111]Fung S,Kwan P,Fabri M,et al.Randomized comparison of tenofovirdisoproxil fumarate vs emtricitabine and tenofovirdisoproxil fumarate in patientswith lamivudine-resistant chronic hepatitis B[J].Gastroenterology,2014,146:980-988.
[112]Lim YS,Yoo BC,Byun KS,et al.Tenofovirmonotherapy versus tenofovir and entecavir combination therapy in adefovirresistant chronic hepatitis B patients with multiple drug failure:results of a randomised trial[J].Gut,2016,65:1042-1051.
[113]Patterson SJ,George J,Strasser SI,et al.Tenofovirdisoproxil fumarate rescue therapy following failure of both lamivudine and adefovir dipivoxil in chronic hepatitis B[J].Gut,2011,60:247-254.
[114]Berg T,Zoulim F,Moeller B,et al.Long-term efficacy and safety of emtricitabine plus tenofovir DF vs.tenofovir DF monotherapy in adefovir-experienced chronic hepatitis B patients[J].JHepatol,2014,60:715-722.
[115]Hou J,Yin YK,Xu D,etal.Telbivudine versus lamivudine in Chinese patientswith chronic hepatitis B:Results at1 year of a randomized,double-blind trial[J].Hepatology,2008,47:447-454.
[116]Liaw YF,Gane E,Leung N,et al.2-Year GLOBE trial results:telbivudine Is superior to lamivudine in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J].Gastroenterology,2009,136:486-495.
[117]Sun J,Xie Q,Tan D,et al.The 104-week efficacy and safety of telbivudine-based optimization strategy in chronic hepatitis B patients:a randomized,controlled study[J].Hepatology,2014,59:1283-1292.
[118]Marcellin P,Chang TT,Lim SG,et al.Long-term efficacy and safety of adefovir dipivoxil for the treatment of hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B[J].Hepatology,2008,48:750-758.
[119]Zeng M,Mao Y,Yao G,etal.A double-blind randomized trial of adefovir dipivoxil in Chinese subjectswith HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B[J].Hepatology,2006,44:108-116.
[120]Hadziyannis SJ,Tassopoulos NC,Heathcote EJ,et al.Longterm therapy with adefovir dipivoxil for HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B for up to 5 years[J].Gastroenterology,2006,131:1743-1751.
[121]Lampertico P,ViganòM,Manenti E,et al.Low resistance to adefovir combined with lamivudine:a 3-year study of 145 lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B patients[J].Gastroenterology,2007,133:1445-1451.
[122]Yao GB,Zhu M,Cui ZY,et al.A 7-year study of lamivudine therapy for hepatitis B virus e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B patients in China[J].JDig Dis,2009,10:131-137.
[123]Liaw YF,Sung JJ,Chow WC,et al.Lamivudine for patients with chronic hepatitis B and advanced liver disease[J].N Engl JMed,2004,351:1521-1531.
[124]Chen CH,Lin CL,Hu TH,et al.Entecavir vs.lamivudine in chronic hepatitis B patients with severe acute exacerbation and hepatic decompensation[J].J Hepatol,2014,60:1127-1134.
[125]Lau GK,Piratvisuth T,Luo KX,et al.Peginterferon Alfa-2a,lamivudine,and the combination for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B[J].N Engl JMed,2005,352:2682-2695.
[126]Janssen HL,van Zonneveld M,Senturk H,et al.Pegylated interferon alfa-2b alone or in combination with lamivudine for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B:a randomised trial[J]. Lancet,2005,365:123-129.
[127]LaiCL,Chien RN,Leung NW,etal.A one-year trial of lamivudine for chronic hepatitis B.Asia Hepatitis Lamivudine Study Group[J].N Engl JMed,1998,339:61-68.
[128]Dienstag JL,Schiff ER,Wright TL,et al.Lamivudine as initial treatment for chronic hepatitis B in the United States [J].N Engl JMed,1999,341:1256-1263.
[129]Lai CL,Gane E,Liaw YF,etal.Telbivudine versus lamivudine in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J].N Engl JMed,2007,357:2576-2588.
[130]Marcellin P,Chang TT,Lim SG,et al.Adefovir dipivoxil for the treatmentof hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B[J].N Engl JMed,2003,348:808-816.
[131]Gish RG,Lok AS,Chang TT,et al.Entecavir therapy for up to 96 weeks in patientswith HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B[J].Gastroenterology,2007,133:1437-1444.
[132]Minde Z,Yimin M,Guangbi Y,et al.Five years of treatment with adefovir dipivoxil in Chinese patients with HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B[J].Liver Int,2012,32:137-146.
[133]Marcellin P,Lau GK,Bonino F,et al.Peginterferon alfa-2a alone,lamivudine alone,and the two in combination in patients with HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B[J].N Engl J Med,2004,351:1206-1217.
[134]Tassopoulos NC,Volpes R,Pastore G,et al.Efficacy of lamivudine in patientswith hepatitis B e antigen-negative/hepatitis B virus DNA-positive(precoremutant)chronic hepatitis B.Lamivudine Precore Mutant Study Group[J].Hepatology,1999,29:889-896.
[135]Hadziyannis SJ,Tassopoulos NC,Heathcote EJ,et al.Adefovir dipivoxil for the treatment of hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B[J].N Engl J Med,2003,348:800-807.
[136]Marcellin P,Bonino F,Lau GK,et al.Sustained response of hepatitis B e antigen-negative patients3 years after treatment with peginterferon alpha-2a[J].Gastroenterology,2009,136:2169-2179,e1-e4.
[137]参加乙型肝炎耐药讨论会专家.核苷和核苷酸类药物治疗慢性乙型肝炎的耐药及其管理[J].中国病毒病杂志,2013,18:1-10.
[138]Sun J,Hou JL,Xie Q,et al.Randomised clinical trial:efficacy of peginterferon alfa-2a in HBeAg positive chronic hepatitis B patients with lamivudine resistance[J].Aliment Pharmacol Ther,2011,34:424-431.
[139]Yapali S,Talaat N,Fontana RJ,et al.Outcomes of patients with chronic hepatitis Bwho do notmeet criteria for antiviral treatment at presentation[J].Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol,2015,13:193-201,e1.
[140]Lok AS,McMahon BJ.Chronic hepatitis B:update 2009[J]. Hepatology,2009,50:661-662.
[141]Liang X,Cheng J,Sun Y,et al.Randomized,three-arm study to optimize lamivudine efficacy in hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B patients[J].JGastroenterol Hepatol,2015,30:748-755.
[142]Reijnders JG,Perquin MJ,Zhang N,et al.Nucleos(t)ide analogues only induce temporary hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion in most patientswith chronic hepatitis B[J].Gastroenterology,2010,139:491-498.
[143]Chi H,Hansen BE,Yim C,et al.Reduced risk of relapse after long-term nucleos(t)ide analogue consolidation therapy for chronic hepatitis B[J].Aliment Pharmacol Ther,2015,41:867-876.
[144]Ryu SH,Chung YH,Choi MH,et al.Long-term additional lamivudine therapy enhances durability of lamivudine-induced HBeAg loss:a prospective study[J].JHepatol,2003,39:614-619.
[145]Wang Y,Thongsawat S,Gane EJ,et al.Efficacy and safety of continuous 4-year telbivudine treatment in patientswith chronic hepatitis B[J].JViral Hepat,2013,20:e37-e46.
[146]Sonneveld MJ,Hansen BE,Piratvisuth T,et al.Responseguided peginterferon therapy in hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B using serum hepatitis B surface antigen levels[J].Hepatology,2013,58:872-880.
[147]Seto WK,Hui AJ,Wong VW,et al.Treatment cessation of entecavir in Asian patients with hepatitis B e antigen negative chronic hepatitis B:amulticentre prospective study[J]. Gut,2015,64:667-672.
[148]Jeng WJ,Sheen IS,Chen YC,et al.Off-therapy durability of response to entecavir therapy in hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B patients[J].Hepatology,2013,58:1888-1896.
[149]Buster EH,Hansen BE,Buti M,et al.Peginterferon alpha-2b is safe and effective in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B patients with advanced fibrosis[J].Hepatology,2007,46:388-394.
[150]Cho JY,Paik YH,Sohn W,et al.Patients with chronic hepatitis B treated with oral antiviral therapy retain a higher risk for HCC compared with patients with inactive stage disease [J].Gut,2014,63:1943-1950.
[151]Yang YJ,Shim JH,Kim KM,etal.Assessmentof current criteria for primary nonresponse in chronic hepatitis B patients receiving entecavir therapy[J].Hepatology,2014,59:1303-1310.
[152]Liu CJ,Chen PJ,Chen DS,et al.Hepatitis B virus reactivation in patients receiving cancer chemotherapy:naturalhistory,pathogenesis,and management[J].Hepatol Int,2013,2:316-326.
[153]Loomba R,Rowley A,Wesley R,et al.Systematic review:the effect of preventive lamivudine on hepatitis B reactivation during chemotherapy[J].Ann Intern Med,2008,148:519-528.
[154]LiHR,Huang JJ,Guo HQ,etal.Comparison ofentecavir and lamivudine in preventing hepatitis B reactivation in lymphoma patients during chemotherapy[J].JViral Hepat,2011,18:877-883.
[155]Perrillo RP,Gish R,Falck-Ytter YT,et al.American gastroenterological association institute technical review on prevention and treatmentof hepatitis B virus reactivation during immunosuppressive drug therapy[J].Gastroenterology,2015,148:221-244.e3.
[156]Hwang JP,LokAS.Management of patientswith hepatitis B who require immunosuppressive therapy[J].Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol,2014,11:209-219.
[157]European Association for the Study of the Liver.EASL Recommendations on Treatment of Hepatitis C 2015[J].JHepatol,2015,63:199-236.
[158]Konstantinou D,Deutsch M.The spectrum of HBV/HCV coinfection:epidemiology,clinical characteristics,viralinteractions and management[J].Ann Gastroenterol,2015,28 (2):221-228.
[159]Liu JY,Sheng YJ,Hu HD,et al.The influence of hepatitis B virus on antiviral treatment with interferon and ribavirin in Asian patients with hepatitis C virus/hepatitis B virus coinfection:ameta-analysis[J].Virol J,2012,9:186.
[160]Kosi L,Reiberger T,Payer BA,et al.Five-year on-treatment efficacy of lamivudine-,tenofovir-and tenofovir+em tricitabine-based HAART in HBV-HIV-coinfected patients[J].J Viral Hepat,2012,19:801-810.
[161]Giorgio A,Francesco M,Claudio A.Access to treatment for HBV infection and itsconsistency with 2008 European guidelines in amulticentre cross-sectional study of HIV/HBV coinfected patients in Italy[J].BMC Research Notes,2013,6:153-160.
[162]Zoutendijk R,Zaaijer HL,de Vries-Sluijs TE,et al.Hepatitis B surface antigen declines and clearance during long-term tenofovir therapy in patients coinfected with HBV and HIV [J].J Infect Dis,2012,206:974-980.
[163]Zhang Y,Hu XY,Zhong S,et al.Entecavir vs lamivudine therapy for naive patients with spontaneous reactivation of hepatitis B presenting as acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. World JGastroenterol,2014,20:4745-4752.
[164]Garg H,Sarin SK,Kumar M,et al.Tenofovir improves the outcome in patientswith spontaneous reactivation of hepatitis B presenting as acute-on-chronic liver failure[J].Hepatology,2011,53:774-780.
[165]Yu S,Jianqin H,WeiW,et al.The efficacy and safety of nucleos(t)ide analogues in the treatmentof HBV-related acuteon-chronic liver failure:a meta-analysis[J].Ann Hepatol,2013,12:364-372.
[166]Zhang X,An Y,Jiang X,et al.Entecavir versus Lamivudine therapy for patients with chronic hepatitis B-associated liver failure:ameta-analysis[J].HepatMon,2014,14:e19164.
[167]Xie F,Yan L,Lu J,et al.Effects of nucleoside analogue on patientswith chronic hepatitis B-associated liver failure:meta-analysis[J].PLoSOne,2013,8:e54773.
[168]Sun P,Dong X,Cheng X,et al.Nucleot(s)ide analogues for hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma after curative treatment:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. PLoSOne,2014,9:e102761.
[169]Yin J,Li N,Han Y,et al.Effect of antiviral treatment with nucleotide/nucleoside analogs on postoperative prognosis of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma:a twostage longitudinal clinical study[J].JClin Oncol,2013,31:3647-3655.
[170]Cholongitas E,Papatheodoridis GV.High genetic barrier nucleos(t)ide analogue(s)for prophylaxis from hepatitis B virus recurrence after liver transplantation:a systematic review [J].Am JTransplant,2013,13:353-362.
[171]Yi NJ,Choi JY,Suh KS,et al.Post-transplantation sequential entecavirmonotherapy following 1-year combination therapy with hepatitis B immunoglobulin[J].JGastroenterol,2013,48:1401-1410.
[172]Teperman LW,Poordad F,Bzowej N,et al.Randomized trial of emtricitabine/tenofovirdisoproxil fumarate after hepatitis B immunoglobulin withdrawal after liver transplantation[J]. Liver Transpl,2013,19:594-601.
[173]Lai CL,Yuen MF.Prevention of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma with antiviral therapy[J].Hepatology,2013,57:399-408.
[174]BzowejNH.Optimal management of the hepatitis B patient who desires pregnancy or is pregnant[J].Curr Hepat Rep,2012,11:82-89.
[175]Pan CQ,Duan ZP,Bhamidimarri KR,et al.An algorithm for risk assessment and intervention ofmother to child transmission of hepatitis B virus[J].Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol,2012,10:452-459.
[176]Zhang H,Pan CQ,Pang Q,et al.Telbivudine or lamivudine use in late pregnancy safely reduces perinatal transmission of hepatitis B virus in real-life practice[J].Hepatology,2014,60:468-476.
[177]Greenup AJ,Tan PK,Nguyen V,et al.Efficacy and safety of tenofovirdisoproxil fumarate in pregnancy to prevent perinatal transmission of hepatitis B virus[J].J Hepatol,2014,61:502-507.
[178]Sarkar M,Terrault NA.Ending vertical transmission of hepatitis B:the third trimester intervention[J].Hepatology,2014,60:448-451.
[179]Della CC,Nobili V,Comparcola D.Management of chronic hepatitis B in children:an unresolved issue[J].JGastroen-Hepatol,2014,29:912-919.
[180]Saadah OI,Sindi HH,Bin-Talib Y,et al.Entecavir treatment of children 2-16 years of age with chronic hepatitis B infection[J].Arab JGastroenterol,2012,13:41-44.
[181]Jonas MM,Chang MH,Sokal E,et al.Randomized,controlled trial of entecavir versus placebo in children with hepatitis B envelope antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B[J]. Hepatology,2016,63:377-387.